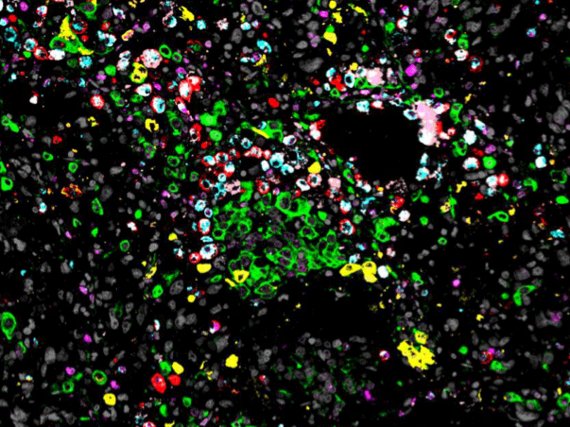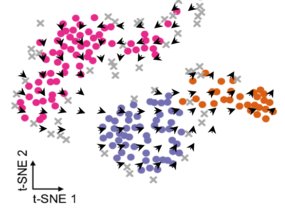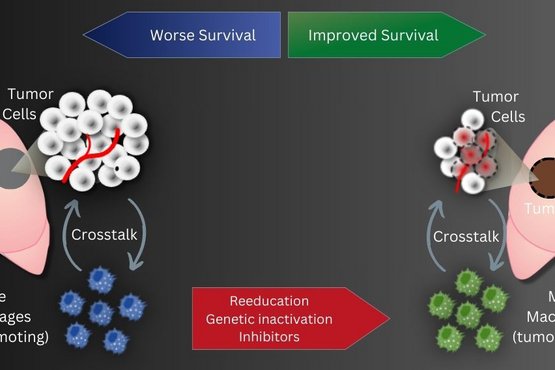
Protein in blood vessels puts tumour cells into deep sleep
Membrane protein PEAR1 prevents the development of metastases
Become part of our team!
Apply now to our International Max Planck Research School for Molecular Organ Biology
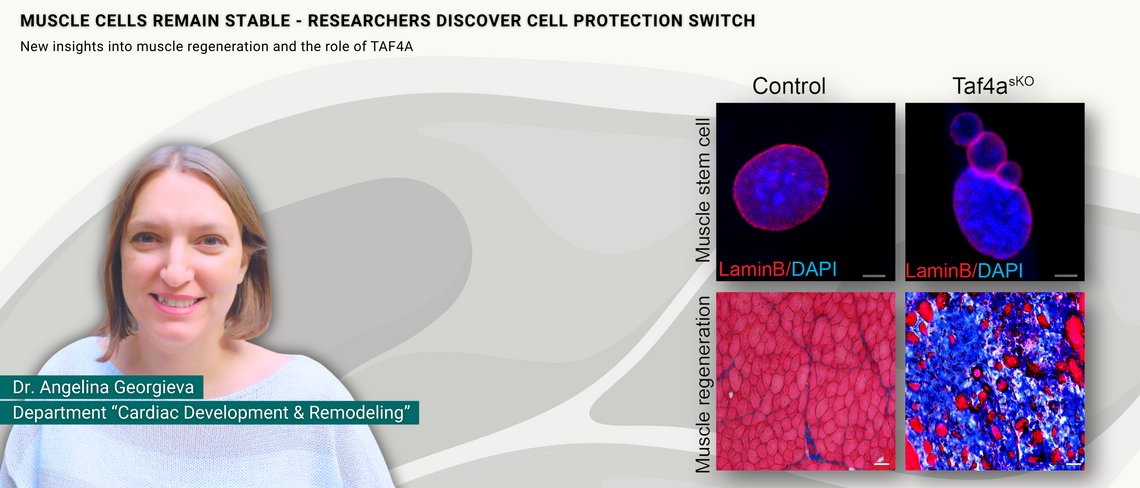
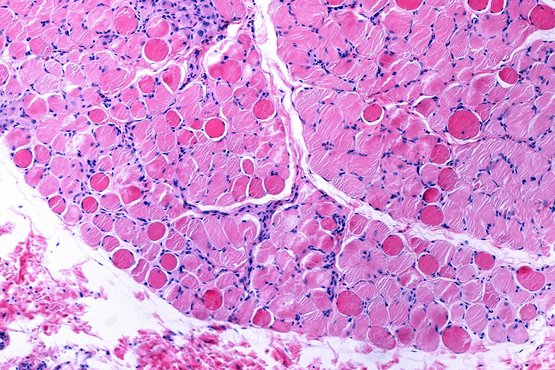
How muscle stem cells keep their nucleus intact to maintain regenerative power
Transcription factor TAF4A preserves nuclei in muscle stem cells and initiates muscle regeneration after injury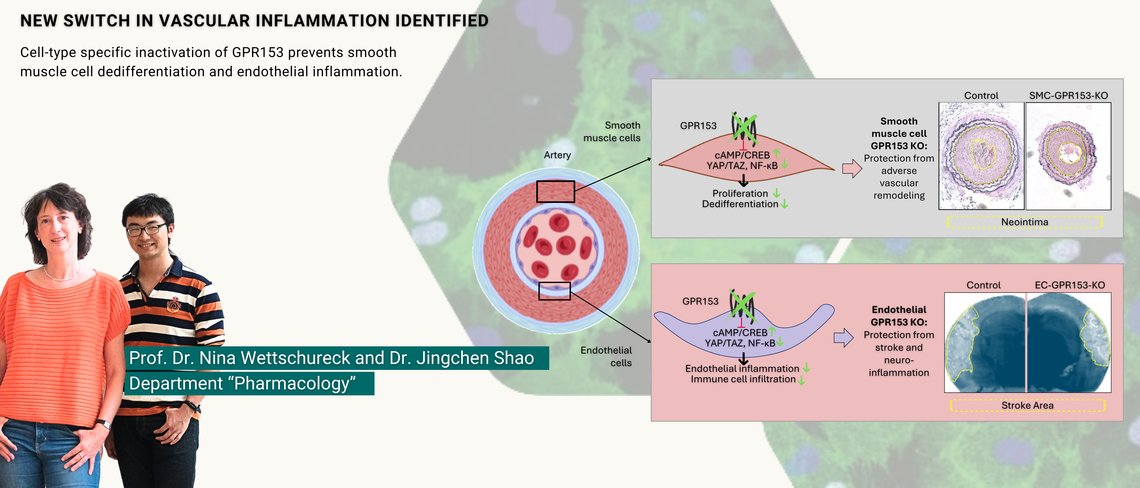
Protein switch in blood vessels exacerbates damage in vascular diseases
GPR153 promotes inflammatory reactions in the vessel wall in response to acute damage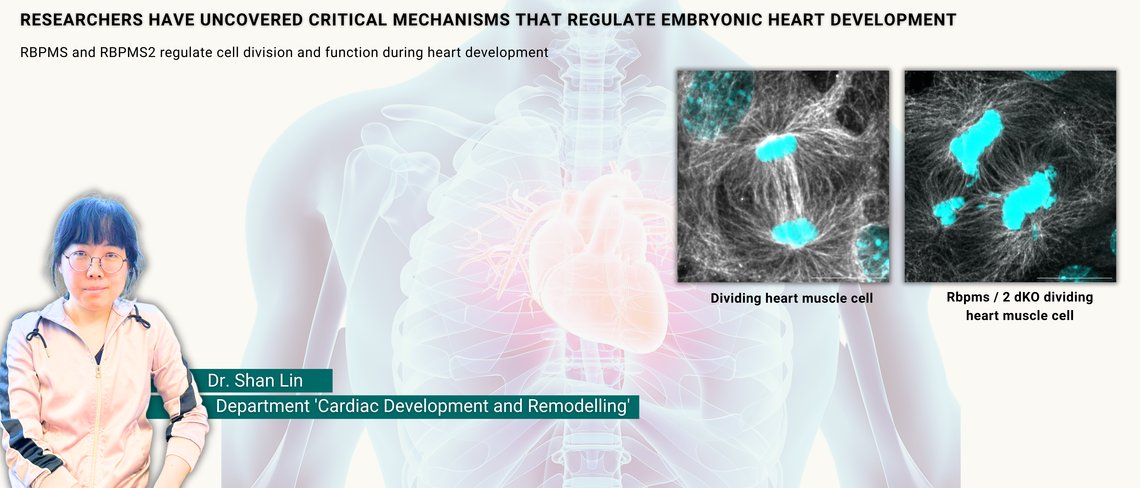
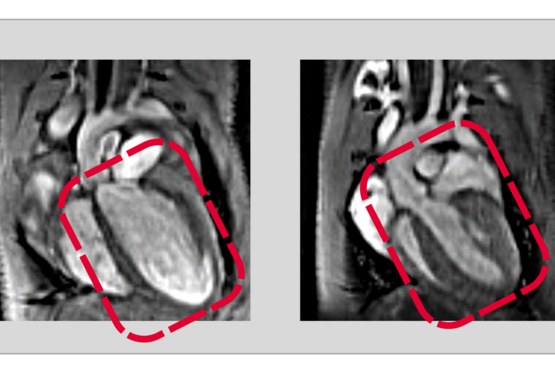
Increasing complexity in the heart: How two related proteins control development of the heart
RBPMS and RBPMS2 regulate cell division and function during heart development
ERC Proof of Concept Grant Awarded to Max Planck Team for RNA-Based Therapy Targeting Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
A team of researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, led by Prof. Dr. Didier Y.R. Stainier, has been awarded a prestigious ERC Proof of Concept (PoC) grant to advance a groundbreaking RNA-based therapeutic strategy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
Targeted activation of 'genetic self-help': Eva Luise Köhler Research Award for Didier Stainier
Didier Stainier, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research in Bad Nauheim, has been awarded this year's Eva Luise Köhler Research Prize for Rare Diseases by the Eva Luise and Horst Köhler Foundation. The prize honours Stainier and his team for their basic research into the muscle disease Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Once again successful in the Excellence Initiative
The Cardiopulmonary Institute (CPI), a joint Cluster of Excellence of the Max Planck Institute in Bad Nauheim and the Universities of Giessen and Frankfurt, has again been honoured as part of the Excellence Initiative of the German federal and state governments and will receive millions in funding for a further seven years.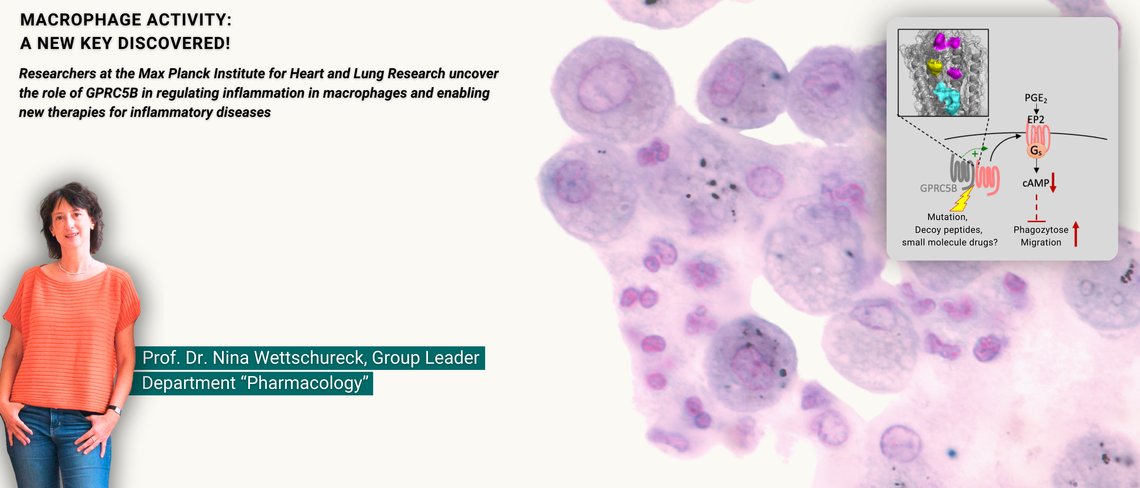
GPRC5B: A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Regulates Macrophage Activity
GPRC5B influences the Prostaglandin Receptor and affects the immune response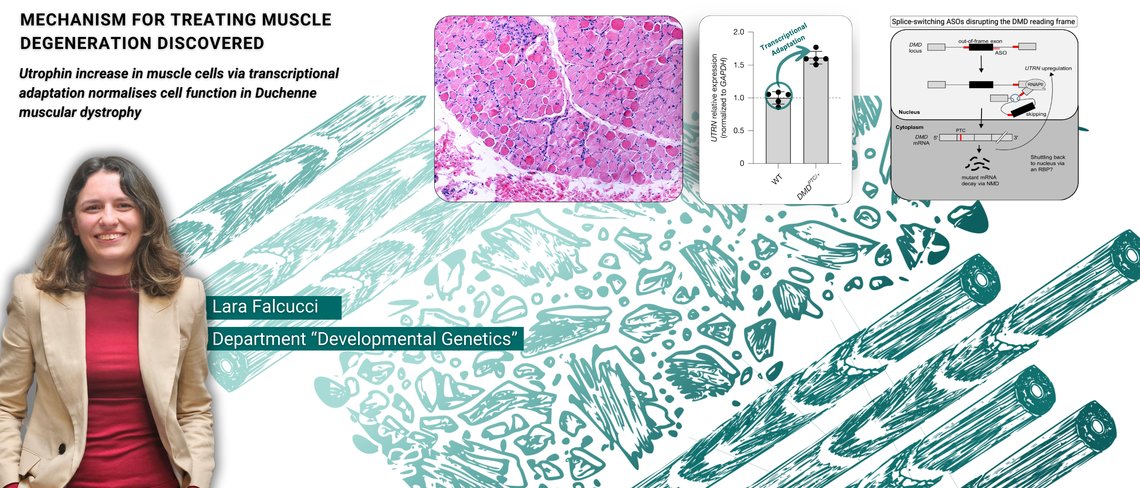
Mechanism for treating muscle degeneration discovered
Utrophin increase in muscle cells via transcriptional adaptation normalises cell function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy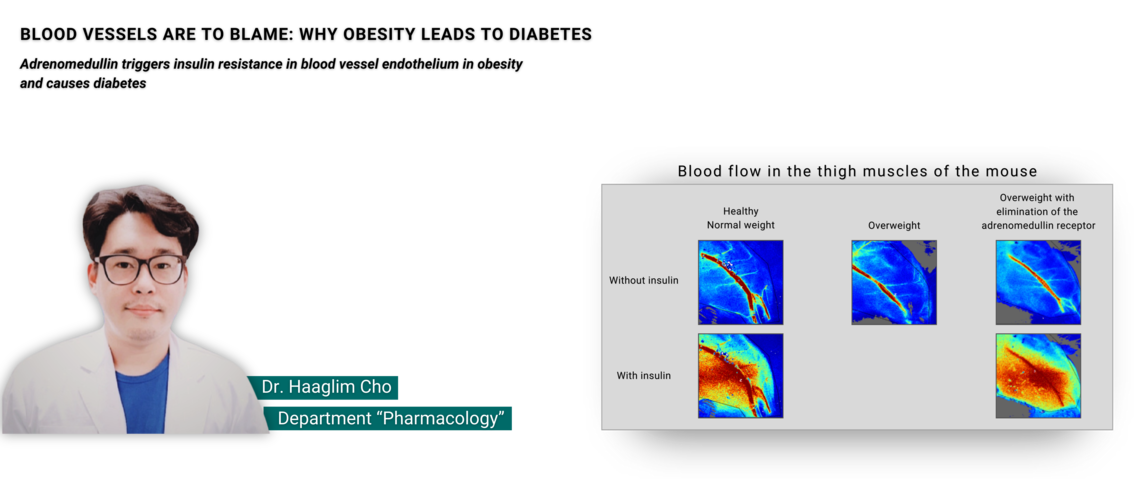
Adrenomedullin causes diabetes in overweight people
The hormone triggers insulin resistance in blood vessel endothelium in obesity
Recycling is also important in the human body. A disrupted protein recycling process can harm heart health.
January 22, 2025An enzyme called Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 5 is a key factor in protein quality in heart muscle cells.

You will find us at two locations in Bad Nauheim: In the New Building, Ludwigstrasse 43, and in the Old Building, Parkstrasse 1.
News from the institute
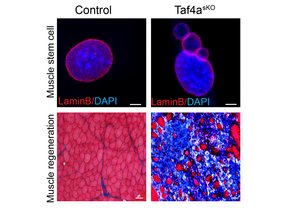
How muscle stem cells keep their nucleus intact to maintain regenerative power
October 13, 2025Transcription factor TAF4A preserves nuclei in muscle stem cells and initiates muscle regeneration after injury

Targeted activation of 'genetic self-help': Eva Luise Köhler Research Award for Didier Stainier
June 21, 2025Didier Stainier has been awarded this year's Eva Luise Köhler Research Prize for Rare Diseases for basic research into the muscle disease Duchenne muscular dystrophy.

Once again successful in the Excellence Initiative
22 May 2025Max Planck Institute again successful together with the Universities of Giessen and Frankfurt in the German government's Excellence Initiative
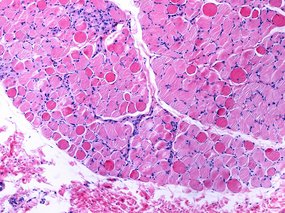
Mechanism for treating muscle degeneration discovered
February 12, 2025Utrophin increase in muscle cells via transcriptional adaptation normalises cell function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
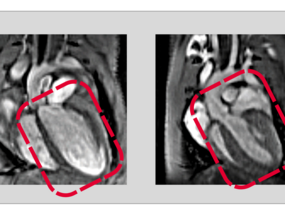
Recycling is also important in the human body. A disrupted protein recycling process can harm heart health.
January 22, 2025An enzyme called Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 5 is a key factor in protein quality in heart muscle cells.
Our Research Departments
Cardiac Development and Remodelling (Dept. I)
Thomas BraunThe research aims to identify the processes governing the development of contractile tissues.
Pharmacology (Dept. II)
Stefan Offermanns
The department investigates cellular signaling pathways and mechanisms of pathophysiological processes in the cardiovascular and metabolic system as well as in cancer.

Developmental Genetics
(Dept. III)
Didier StainierInvestigates questions related to organogenesis including cell differentiation, tissue morphogenesis, organ homeostasis and function, as well as organ regeneration.
Our Research Groups
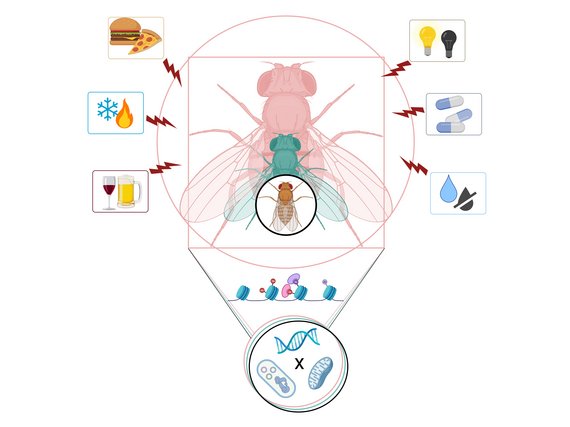
Epigenetics
Lei GuThe Gu laboratory combines bioinformatics, epigenomics cancer biology, fly genetics and mass spectrum to identify and investigate roles of novel epigenetic modifications.
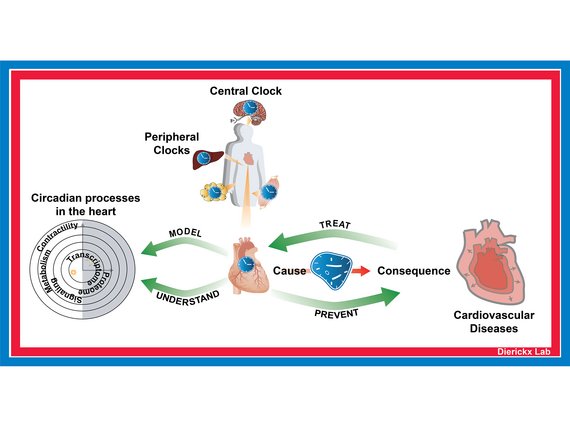
Circadian rhythms in heart metabolism
Pieterjan DierickxThe Dierickx lab is interested in how the circadian clock drives rhythmic processes in the heart. Circadian rhythms coordinate many aspects of behavior and physiology to be in synchrony with the 24-hour rotation of the earth.
Our Emeritus Group
Our Scientific Service Groups
News
Postdoctoral Research Fellow (f/m/d)
January 16, 2026
PhD Student (m/f/d)
January 16, 2026
Ten fully funded PhD positions | Molecular Organ Biology
December 01, 2025